EC2
Features
- EC2 = Elastic Cloud Compute -> Infrastructure as a Service
- Rent virtual machines
- Store data on virtual drives (EBS)
- Load distribution across machines (ELB)
- Scaling the services using auto-scaling group (ASG)
EC2 sizing and configuration options
- OS
- CPU
- RAM
- Storage space (EBS &EFS)
- Network card speed
- Firewall rules
- Bootstrap script : EC2 user data
Bootstrapping
- To launch commands when the machine starts
- Carried out using EC2 User data scripts
- Script runs only once at the instance's first start
- Used to automate boot tasks such as
- install updates
- install software
- download common files from internet
- EC2 User data script runs under root user (sudo rights)
EC2 Instance Types
- General Purpose
- great for diversity of workloads (web services and code repos)
- good balance between compute, memory and networking
- example : t2.micro
- Compute Optimised
- Good for compute intensive tasks
- batch processing workloads
- media transcoding
- high performance web servers
- high performance computing
- scientific modelling & machine learning
- dedicated gaming servers
- Example C6g, C6gn, C5, C5a, etc
- Memory Optimised
- Fast performance for workloads processing large data sets
- Use cases:
- high performance, relational/non-relational databases
- distributed web scale cache stores
- In-memory databases optimised for BI
- Apps performing real-time processing of big unstructured data
- Example : R-series, X, Z, high memory
- Storage Optimised
- Great for storage intensive tasks requiring high sequential read/write access to large data sets on local storage
- Use cases:
- high frequency online transaction processing (OLTP) systems
- relational and NoSQL databases
- Cache for in-memory databases
- Data warehousing apps
- distributed file systems
- Example : I-series, D and H
AWS naming convention : Using example of m5.2xlarge
m : instance class
5 : generation (incremented as AWS improves them over time)
2xlarge : size within the instance class (indicates the size of memory, cpu, etc)
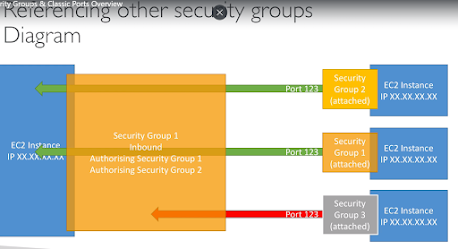
Security Groups
- Fundamental of network security of AWS
- controls how traffic is allowed into or out of EC2 instances.
- only contain "allow" rules
- rules can reference by IP or other security groups
- act as "firewall" on EC2 instances
- they regulate :
- access to ports
- authorised IP ranges - IPv4 and IPv6
- control of inbound network
- control of outbound network
- can be attached to multiple instances
- instances can have multiple security groups
- closely coupled with the region/VPC combination
- exists as a "firewall" outside of the EC2 instance
- Good practice to maintain one separate security group for SSH access
- if application is not accessible (time outs), its probably a security group issue
- However, "connection refused" indicates that traffic went through but application errored out or didn't launch
- By default, all inbound traffic is blocked and all outbound traffic is authorised
Classic Ports to know
- 22 = SSH (secure shell) - log into a Linux instance
- 21 = FTP - upload file into a file share
- 22 = SFTP - upload files using SSH
- 80 = HTTP - to access unsecured websites
- 443 = HTTPS - access secured websites
- 3389 = RDS (remote desktop protocol) - log into a Windows instance

No comments:
Post a Comment